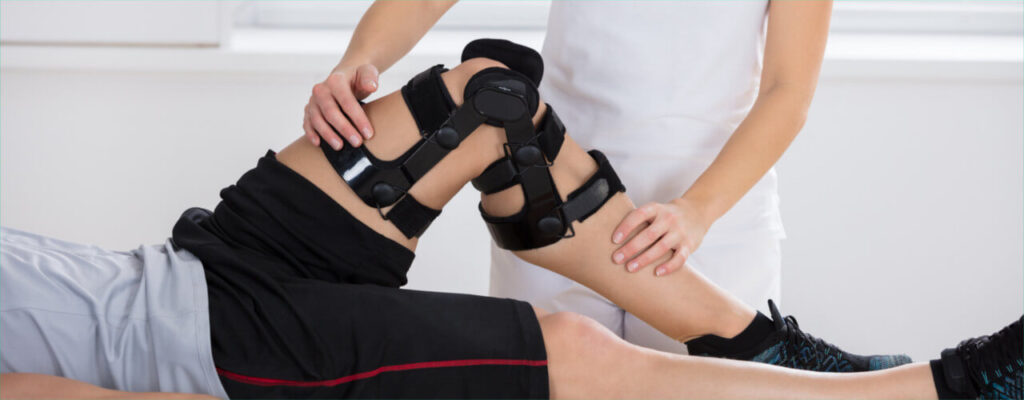
Knee replacement surgery is one of the most commonly performed procedures by orthopedic surgeons around the world. It provides lasting relief for patients experiencing chronic joint pain and limited mobility.
While the surgery itself is a critical step, true recovery begins afterward. Knee replacement recovery requires a structured rehabilitation plan that includes physiotherapy, strength-building, and balance training.
Physiotherapy forms the foundation of this process, helping patients regain movement, build muscle, and restore independence. Its role becomes even more essential as patients progress toward complete mobility.
Following a knee replacement surgery patients need physiotherapy due to its essential role in the recovery process. During knee replacement surgery the medical team removes damaged cartilage and bone which they then substitute with prosthetic parts. The operation creates disturbances that negatively impact the joint structure and disturb the mechanics of muscles and ligaments and knee coordination. Physiotherapy helps by:
Restoring range of motion
Every individual recovers differently from knee replacement but the process can be organized into the following stages:

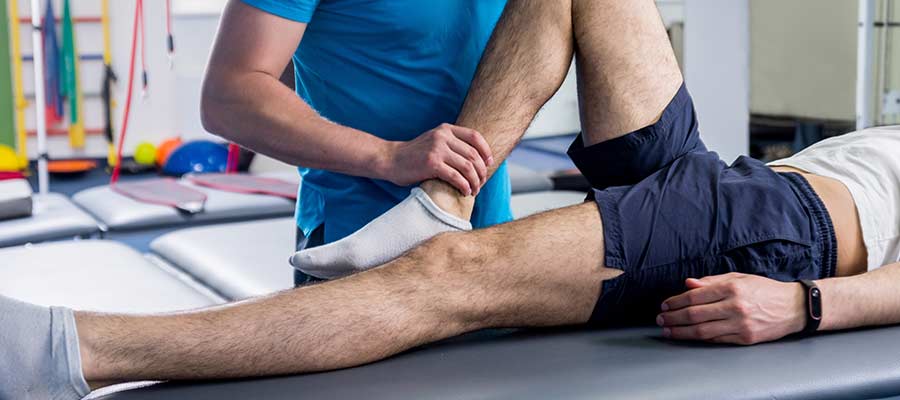
Soft tissue mobilization together with passive stretching through Manual Therapy reduces adhesions and scar tissue formation. Limited passive procedures serve to recover joint mobility through gentle tissue movements.
Water-based exercises play a key role in rehabilitation, especially for patients managing weight or dealing with balance issues. The buoyancy of water reduces stress on the joints while still offering effective resistance for strength training.
Surgical recovery requires focused training in proper walking and balance techniques. Key areas of therapy include step length, weight shifting, and balance reactions—all essential for preventing falls.
Home Exercise Programs (HEPs) are introduced early in the recovery process and evolve as healing progresses. Patients are encouraged to:
Perform daily exercises
Track pain levels and note any improvements
Monitor swelling, flexibility, and muscle strength on their own
Pain Management: Controlled through medication, ice, and physiotherapy
Early movement prevents joint stiffness which occurs because of delayed movements.
Wound swelling can be managed through elevation combined with compression techniques while normal physical activity plays a helpful role.
The recovery process will take time so people need to stay consistent each day to achieve lasting success.
Persistent swelling or warmth around the joint
The knee should not move beyond a predefined angle because of medical restrictions.
The joint pain becomes severe despite using both prescription drugs and periods of complete rest.
Look for symptoms of infection that include fever together with red streaks and discharge from the area.
Hold steady with your physio therapy exercises
Each recovery journey remains distinctive from the others so resist comparing your recovery progress with others.
Physics and medicine recommend using assistive devices until you feel strong enough for walking alone.
Observe your physical condition then take breaks when necessary
Keep all follow-up appointments
A: Employees can return to stationary work duties after six weeks of recovery whereas more demanding roles require three months or longer.
A: The prosthetic joint tends to produce mild clicking sounds that should not cause any discomfort.
A: Most surgical professionals advise patients to stay away from kneeling activities during a minimum of several months. Always check with your doctor.
A: The majority of patients show 80–90% recovery at the 3-month mark while total recovery usually needs a full year for completion.